Vulnerability Report - October 2025
Introduction
This vulnerability report has been generated using data aggregated on Vulnerability-Lookup, with contributions from the platform’s community.
It highlights the most frequently mentioned vulnerability for October 2025, based on sightings collected from various sources, including MISP, Exploit-DB, Bluesky, Mastodon, GitHub Gists, The Shadowserver Foundation, Nuclei, SPLOITUS, Metasploit, and more. For further details, please visit this page.
The Month at a Glance
The October 2025 cybersecurity landscape has seen significant activity, with several high-profile vulnerabilities garnering attention due to widespread sightings and critical severity ratings. Analysis of the top 10 vulnerabilities of the month highlights major exposures across enterprise software, server platforms, and popular development tools.
At the forefront is CVE-2025-61882, affecting Oracle Concurrent Processing, which accumulated 241 sightings and is classified as critical with a VLAI confidence score of 0.9963. Close behind is CVE-2025-59287, impacting Microsoft Windows Server 2019, with 235 sightings and critical severity (confidence 0.9565). Redis also experienced notable issues with CVE-2025-49844, recording 106 sightings and critical classification, while Unity3D’s Unity Editor (CVE-2025-59489) and Oracle Configurator (CVE-2025-61884) were flagged as high-risk vulnerabilities with 98 and 95 sightings, respectively. Adobe Commerce’s CVE-2025-54236 further highlights the ongoing risk to e-commerce platforms with 94 sightings and critical rating. Other notable entries include ASP.NET Core 8.0 (CVE-2025-55315), D-Link DIR-645 (CVE-2015-2051), Cisco IOS (CVE-2025-20352), and Zyxel p660hn-t1a_v1 (CVE-2017-18368), which remain high or critical in severity.
In parallel, updates to major Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalogs, particularly the CISA list, reveal additional critical entries. VMware VCF operations (CVE-2025-41244) and XWiki Platform (CVE-2025-24893) are newly listed, alongside multiple Dassault Systèmes DELMIA Apriso vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-6205, CVE-2025-6204), Oracle Configurator (CVE-2025-61884), and Adobe Commerce (CVE-2025-54236), all showing high or critical severity. Microsoft continues to feature prominently with Windows Server 2019 (CVE-2025-59287) and older Windows versions under active exploitation. Other newly listed KEVs include Apple macOS (CVE-2022-48503), Kentico Xperience (CVE-2025-2746, CVE-2025-2747), and various security flaws in third-party software like MOTEX Lanscope Endpoint Manager and Rapid7 Velociraptor.
The report also identifies unpublished vulnerabilities detected in the wild. Significant examples include a critical Chrome V8 JavaScript engine flaw (CVE-2025-12036) observed in 12 instances, and multiple remote code execution vulnerabilities in 7-Zip (CVE-2025-11001, CVE-2025-11002). Other unpublished exposures involve OpenCMS XXE attacks, and AMD CPU microcode verification flaws.
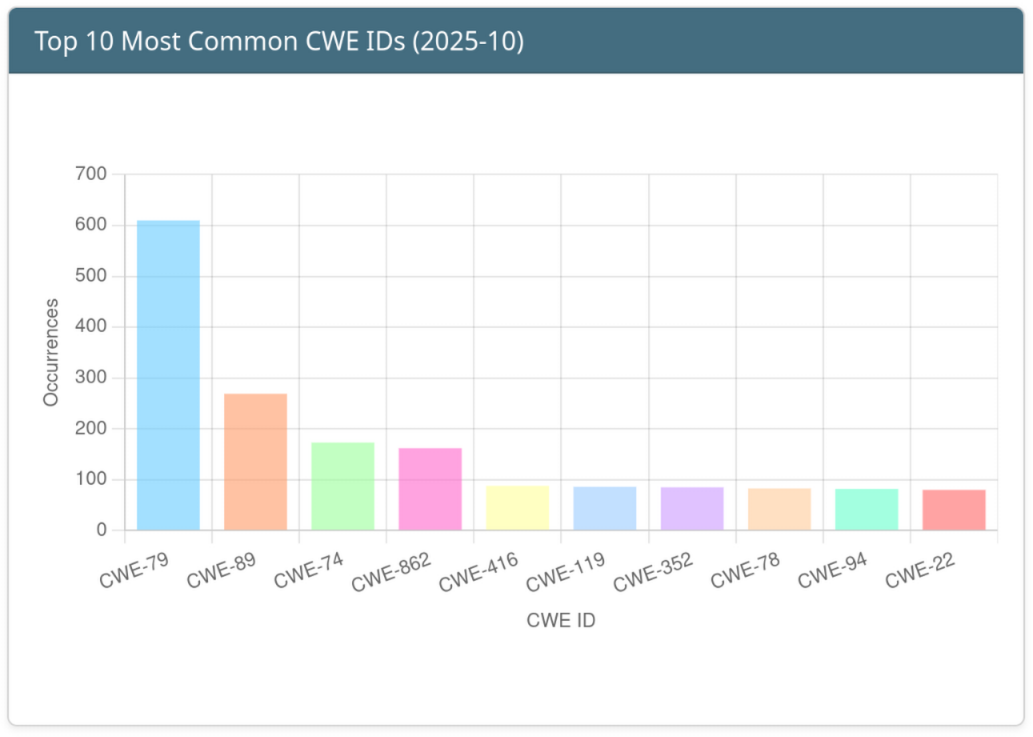
Top weaknesses of the month, summarized via CWE categories, reveal recurring patterns in software development and deployment, emphasizing common attack vectors that continue to be exploited across industries. Contributors’ insights provided context for ongoing campaigns and incidents, including quarterly security notifications from F5, OpenSSL advisories, and the identification of Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) for CVE-2025-59287. Notably, speculation links recent Red Hat OpenShift AI compromises to recently disclosed vulnerabilities, underlining the importance of proactive patching and monitoring.
Overall, October’s data underscores a continued trend of critical vulnerabilities affecting widely used software and enterprise systems, with both published and unpublished flaws actively exploited. Organizations are strongly encouraged to review KEV listings, prioritize patching based on severity and exposure, and monitor sightings to mitigate immediate threats. The prominence of high-severity vulnerabilities in core infrastructure and cloud services emphasizes the need for continuous vigilance and timely vulnerability management.
This month’s report features a new section dedicated to Sightings Forecast using a Poisson regression model.
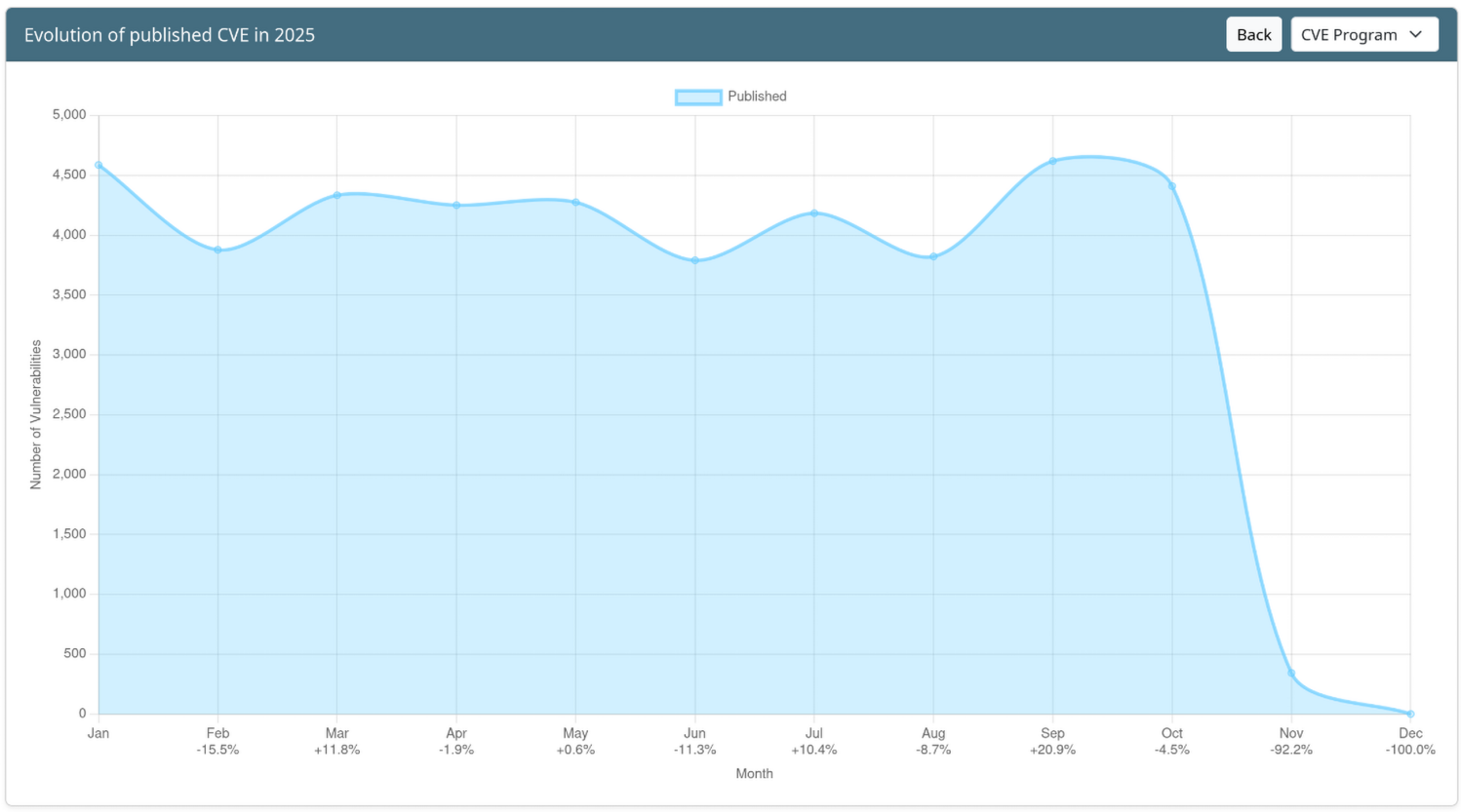
Evolution of published CVE in 2025
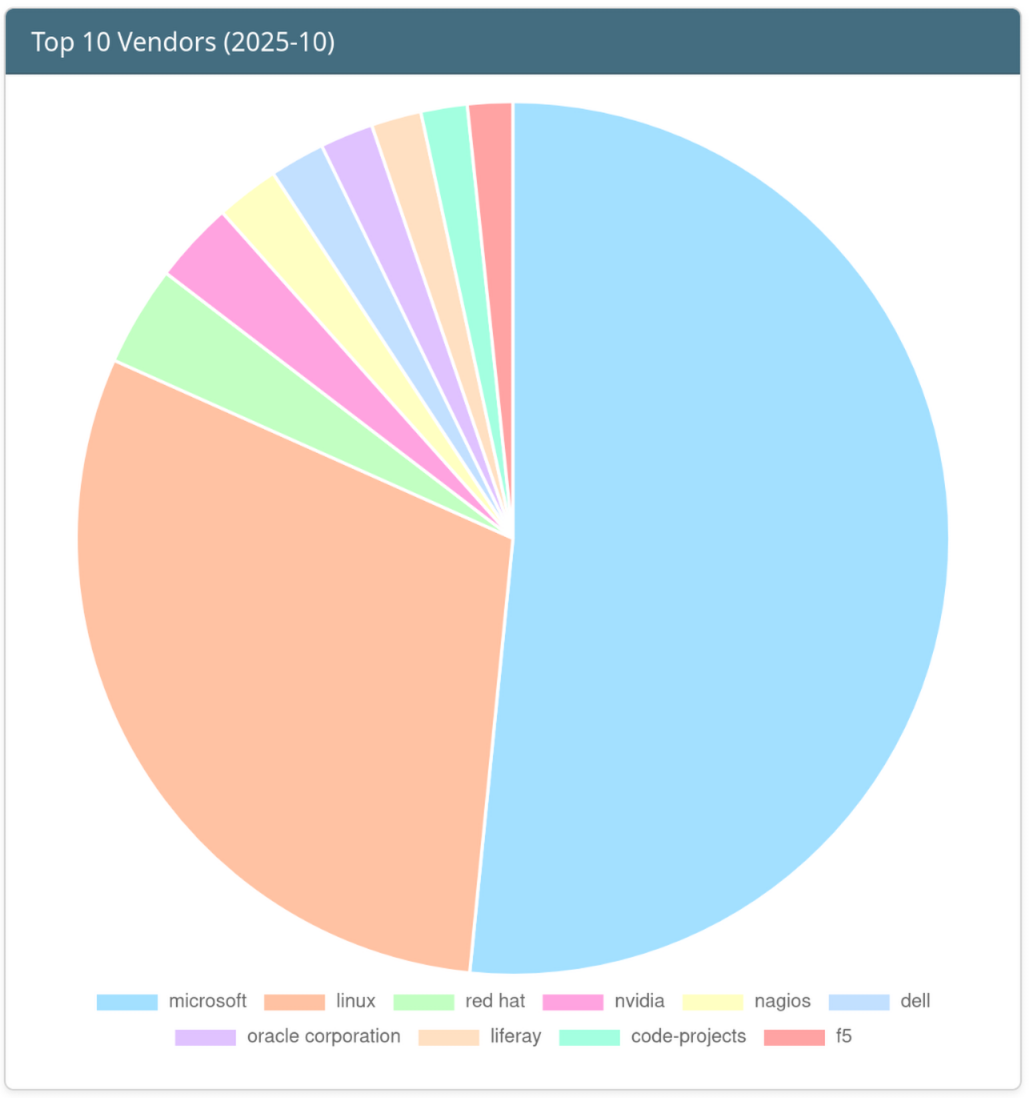
Top 10 Vendors of the Month
Top 10 vulnerabilities of the Month
| Vulnerability | Sighting Count | Vendor | Product | VLAI Severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
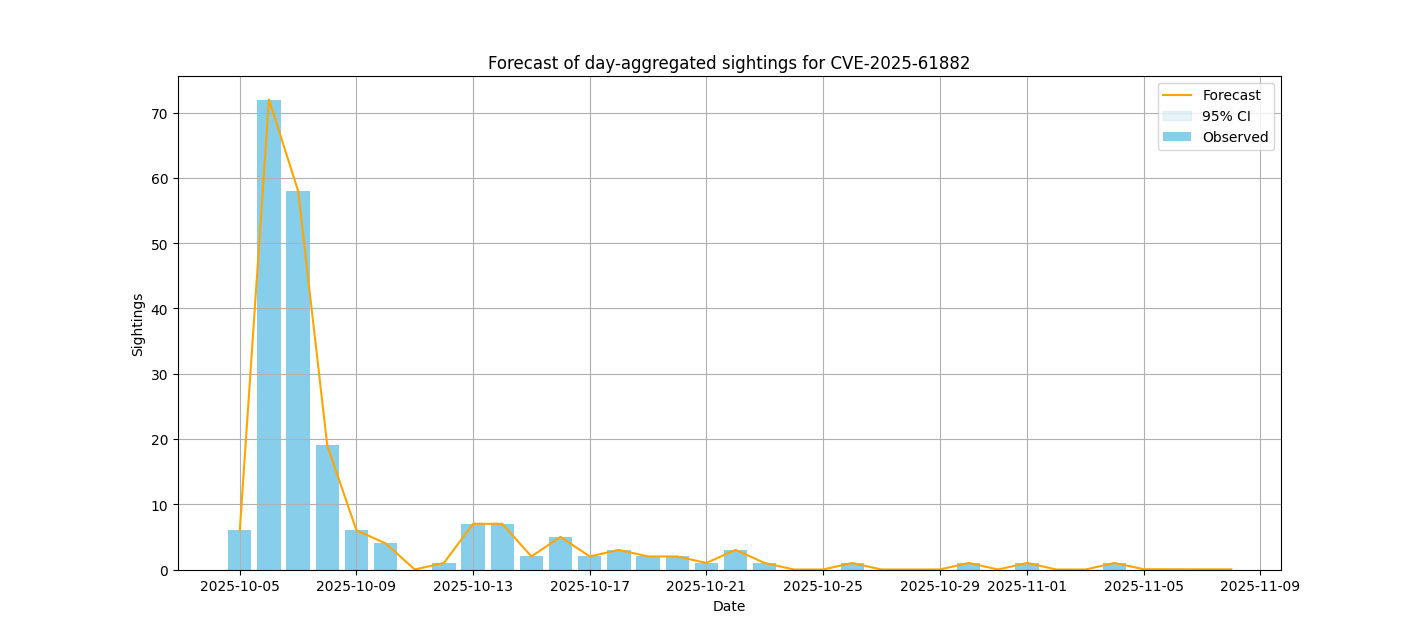
| CVE-2025-61882 | 241 | Oracle Corporation | Oracle Concurrent Processing | Critical (confidence: 0.9963) |
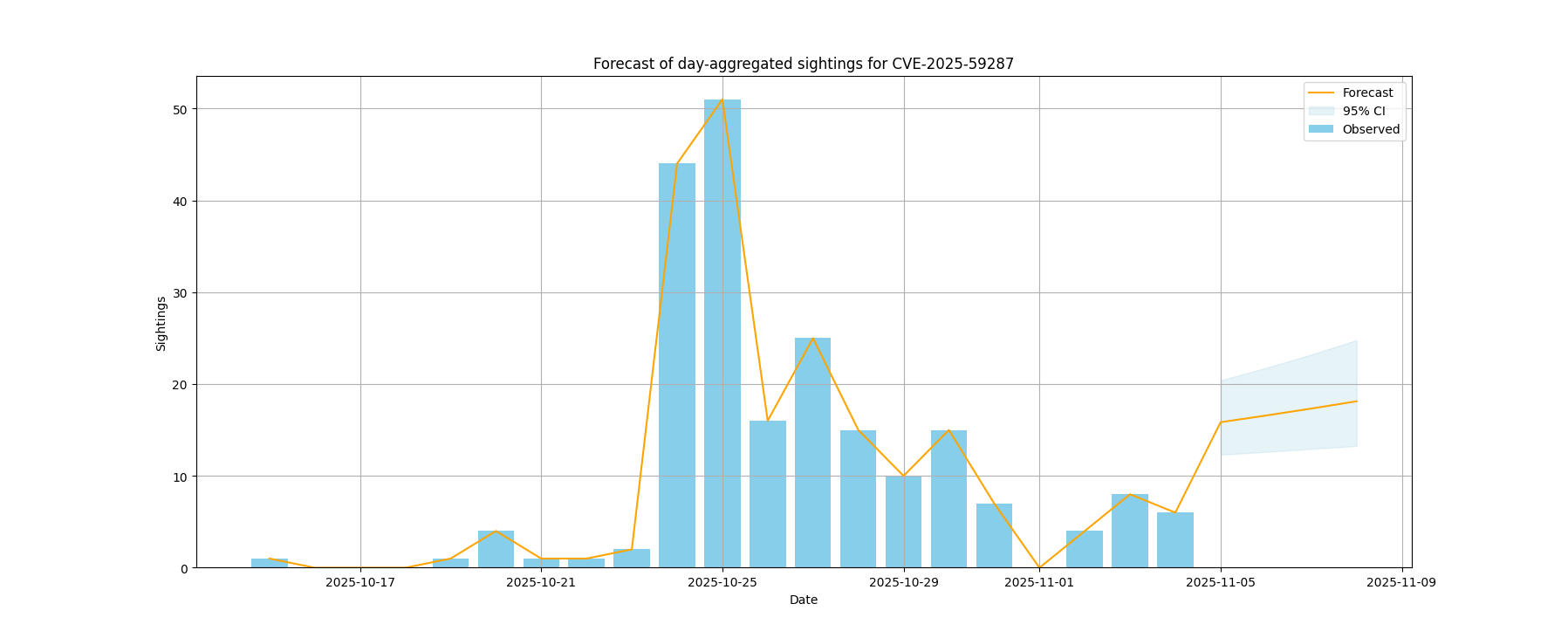
| CVE-2025-59287 | 235 | Microsoft | Windows Server 2019 | Critical (confidence: 0.9565) |
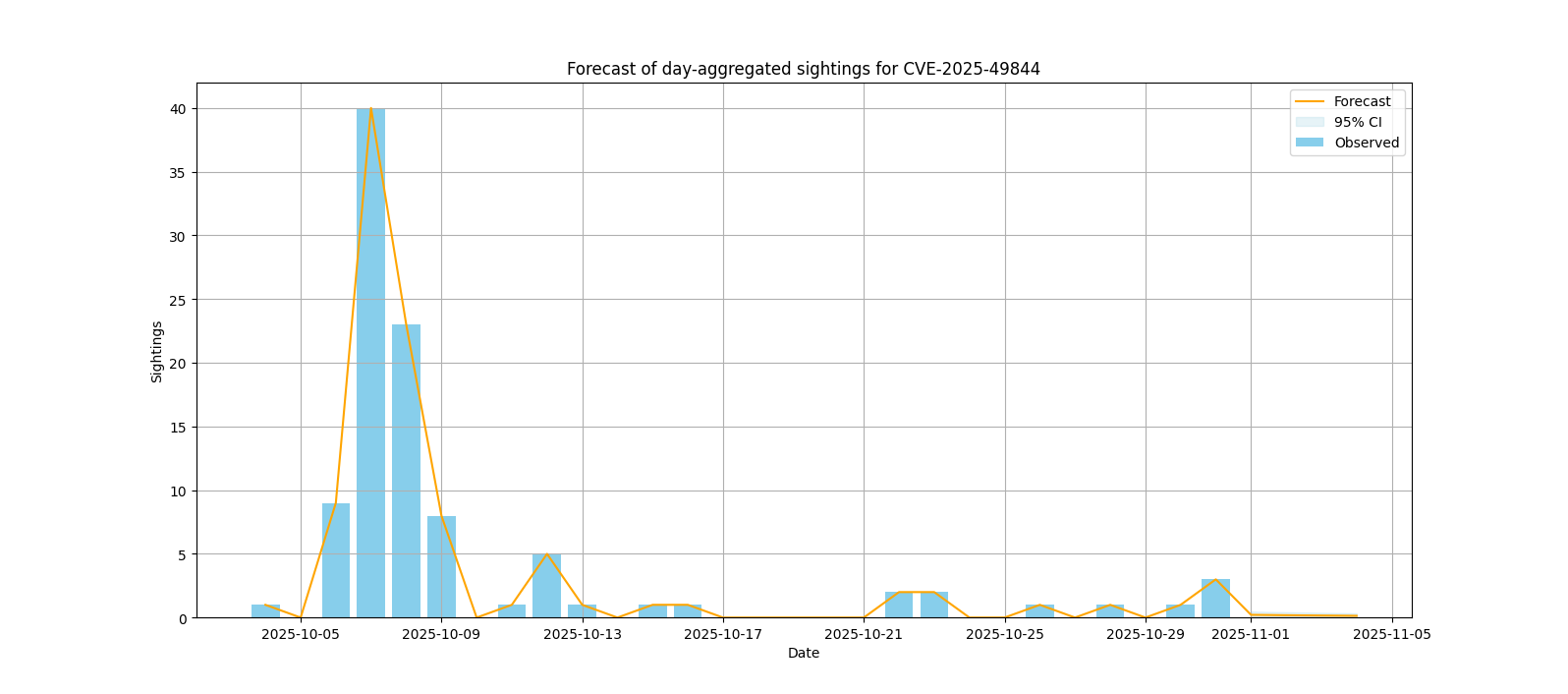
| CVE-2025-49844 | 106 | redis | redis | Critical (confidence: 0.6333) |
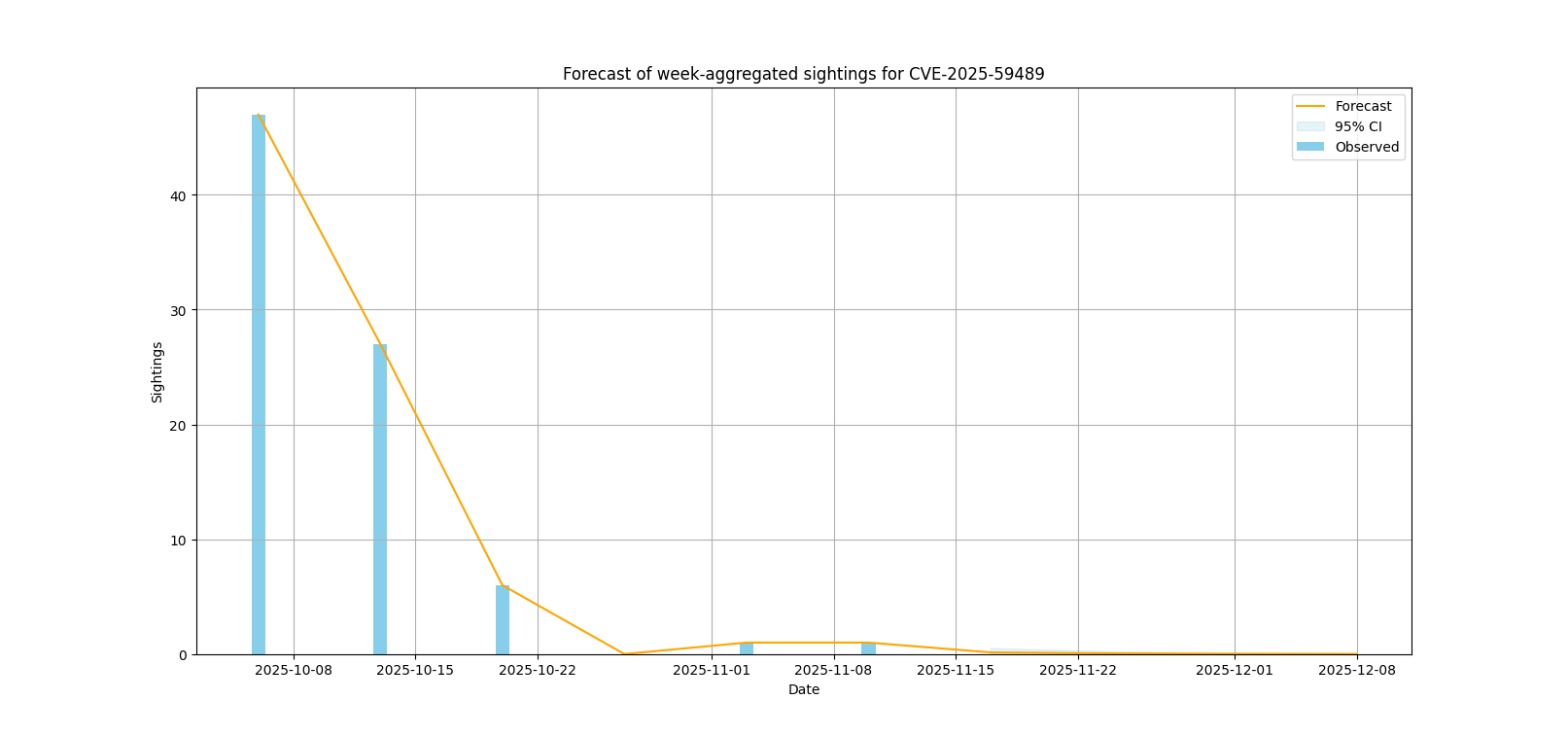
| CVE-2025-59489 | 98 | Unity3D | Unity Editor | High (confidence: 0.951) |
| CVE-2025-61884 | 95 | Oracle Corporation | Oracle Configurator | High (confidence: 0.9969) |
| CVE-2025-54236 | 94 | Adobe | Adobe Commerce | Critical (confidence: 0.9955) |
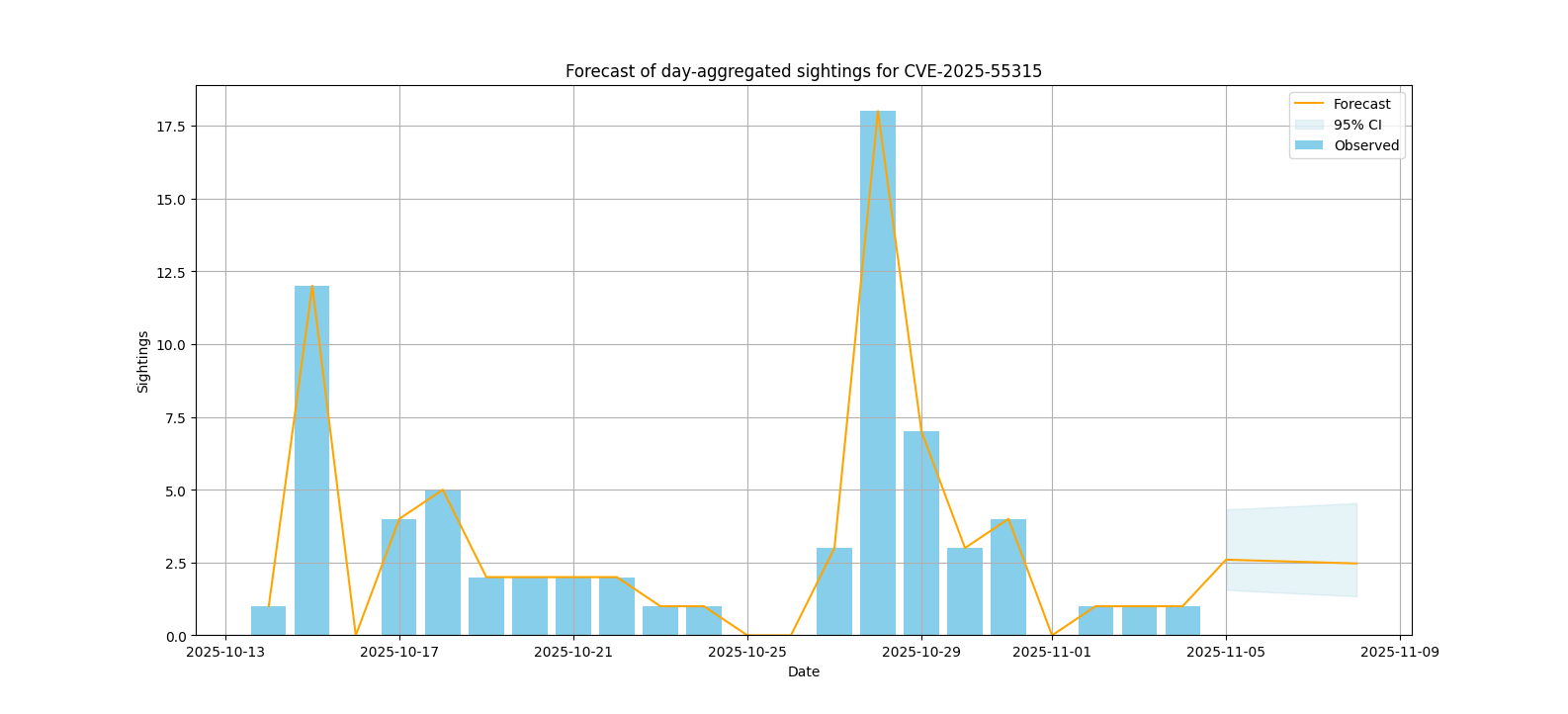
| CVE-2025-55315 | 75 | Microsoft | ASP.NET Core 8.0 | High (confidence: 0.5387) |
| CVE-2015-2051 | 64 | dlink | dir-645 | High (confidence: 0.744) |
| CVE-2025-20352 | 63 | Cisco | IOS | High (confidence: 0.9917) |
| CVE-2017-1836 | 63 | zyxel | p660hn-t1a_v1 | Critical (confidence: 0.9559) |
Sightings forecast
The following visualizations represent the forecasted number of sightings for various vulnerabilities, using a Poisson regression model with adaptive daily/weekly granularity.
Known Exploited Vulnerabilities
New entries have been added to major Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalogs.
CISA
ENISA
No new entry in October.
Top 10 Weaknesses of the Month
Click the image for more information.
Unpublished Vulnerabilities in the Wild
Sightings detected between 2025-10-01 and 2025-10-31 that are associated with unpublished vulnerabilities.
| Vulnerability ID | Occurrences | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| CVE-2025-12036 | 12 | A New Critical Chrome V8 JavaScript Engine Flaw Enables Attackers to Execute Remote Code on Vulnerable Systems |
| CVE-2025-11001 | 9 | 7-Zip Arbitrary Code Execution |
| CVE-2023-42344 | 7 | OpenCMS Unauthenticated XXE Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-35347 | 4 | AMD CPU Microcode Signature Verification Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-10230 | 4 | Samba security releases for CVE-2025-10230 and CVE-2025-9640 |
| CVE-2025-11002 | 4 | 7-Zip ZIP File Parsing Directory Traversal Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| GHSA-8h43-rcqj-wpc6 | 3 | Quotes control bypass in Mastodon |
| CVE-2025-12490 | 2 | Netgate pfSense CE Suricata Path Traversal Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-24293 | 2 | Rails - Active Storage allowed transformation methods that were potentially unsafe |
Insights from Contributors
- F5 - K000156572: Quarterly Security Notification (October 2025)
- OpenSSL Security Advisory
- Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) for CVE-2025-59287
- Growing speculation that the Red Hat compromise may be linked to a recently disclosed vulnerability in Red Hat OpenShift AI
Thank you
Thank you to all the contributors and our diverse sources!
If you want to contribute to the next report, you can create your account.
Feedback and Support
If you have suggestions, please feel free to open a ticket on our GitHub repository. Your feedback is invaluable to us!
https://github.com/vulnerability-lookup/vulnerability-lookup/issues/
Funding

The main objective of Federated European Team for Threat Analysis (FETTA) is improvement of Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) products available to the public and private sector in Poland, Luxembourg, and the European Union as a whole.
Developing actionable CTI products (reports, indicators, etc) is a complex task and requires an in-depth understanding of the threat landscape and the ability to analyse and interpret large amounts of data. Many SOCs and CSIRTs build their capabilities in this area independently, leading to a fragmented approach and duplication of work.
The Computer Incident Response Center Luxembourg (CIRCL) is a government-driven initiative designed to provide a systematic response facility to computer security threats and incidents. The organization brings to the table its extensive experience in cybersecurity incident management, threat intelligence, and proactive response strategies. With a strong background in developing innovative open source cybersecurity tools and solutions, CIRCL’s contribution to the FETTA project is instrumental in achieving enhanced collaboration and intelligence sharing across Europe.